Before the first lecture: installation and setup
1. Installing R and RStudio
1.1 Installing R
We start with installing the latest version of R (3.6.1 as of September 9). R itself is similar to an engine and chassis of a car, that is a bare minimum so that you can start driving. You need to follow steps below:
- Visit https://cran.r-project.org and click on “Download R for …”, where … coresponds to your operating system.
- Depending on the operating system:
- For Mac: download “R-3.6.1.pkg”, open this file, and install R
- For Widnows: click on “base”, download the .exe file, open it, and install R
Check yourself: Open R application. In the console you will see something as follows:
R version 3.6.1 (2019-07-05) -- "Action of the Toes"
Copyright (C) 2019 The R Foundation for Statistical Computing
Platform: x86_64-apple-darwin15.6.0 (64-bit)
R is free software and comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY.
You are welcome to redistribute it under certain conditions.
Type 'license()' or 'licence()' for distribution details.
Natural language support but running in an English locale
R is a collaborative project with many contributors.
Type 'contributors()' for more information and
'citation()' on how to cite R or R packages in publications.
Type 'demo()' for some demos, 'help()' for on-line help, or
'help.start()' for an HTML browser interface to help.
Type 'q()' to quit R.
Note: If you are a Mac user and you see similar to the following warning messages during the startup
During startup - Warning messages:
1: Setting LC_CTYPE failed, using "C"
2: Setting LC_COLLATE failed, using "C"
3: Setting LC_TIME failed, using "C"
4: Setting LC_MESSAGES failed, using "C"
5: Setting LC_PAPER failed, using "C"
[R.app GUI 1.50 (6126) x86_64-apple-darwin9.8.0]
WARNING: You're using a non-UTF8 locale, therefore only ASCII characters will work. Please read R for Mac OS X FAQ (see Help) section 9 and adjust your system preferences accordingly. [History restored from /Users/nemo/.Rapp.history]
you need to follow steps below:
- Open Terminal
- Write or paste in:
defaults write org.R-project.R force.LANG en_US.UTF-8 - Close Terminal
1.2 Installing RStudio
Caution: Install RStudio only once R has been installed and only in this order.
RStudio is an integrated development environment for R. Following up our exaple of the car, RStudio is similar to additional parts, such as exterior, interior, air conditioner, etc. You can drive the vehicle withour them, but life is much simpler and pleasent if they are present.
We will install the free version:
- Visit https://www.rstudio.com/products/rstudio/download/#download.
- Click on the respective version of your operating system, this will start the downloading process.
- Open the file and install.
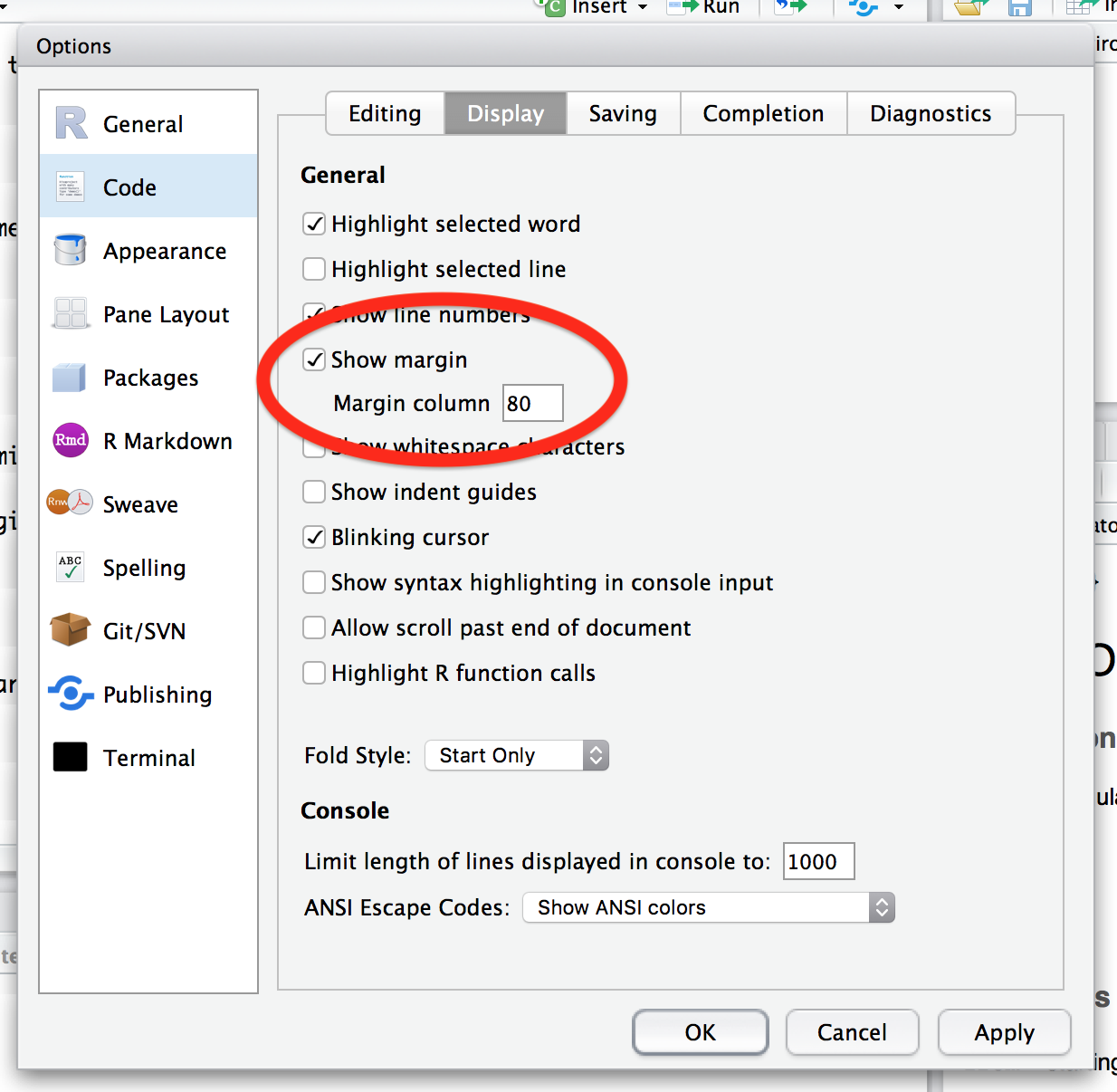
Note: To improve the quality of the code, we will limit the length of lines to 80 symbols. To display the margin in RStudio sourse editor:
- Open RStudio
- Go to Tools -> Global Options… -> Code -> Display
- Click on “Show margin”
- Set “Margin column” to 80
Check yourself: Open RStudio application. In the console you will see something as follows:
R version 3.6.1 (2019-07-05) -- "Action of the Toes"
Copyright (C) 2019 The R Foundation for Statistical Computing
Platform: x86_64-apple-darwin15.6.0 (64-bit)
R is free software and comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY.
You are welcome to redistribute it under certain conditions.
Type 'license()' or 'licence()' for distribution details.
Natural language support but running in an English locale
R is a collaborative project with many contributors.
Type 'contributors()' for more information and
'citation()' on how to cite R or R packages in publications.
Type 'demo()' for some demos, 'help()' for on-line help, or
'help.start()' for an HTML browser interface to help.
Type 'q()' to quit R.
1.3 Installing packages
Note: Packages can be installed from both R and RStudio. The installed RStudio is not required.
In this course we will utilize a number of packages. If a package is published on CRAN, then the procedure of installing the package is straightforward:
- Open RStudio
- In the console execute the following command:
install.packages("package_name"), wherepackage_nameis the name of the desired package (e.g., “ggplot2”).
Several packages, however, would have only development version (or simply be not published on CRAN). Then, knowing the GitHub link to the repo, one could follow the steps below:
- Install
devtoolspackage (if it has not yet been installed) as usual (as shown above). - Type
devtools::install_github("username/repo")and hit the Enter/return key to execute the command in the console, whereusernameis the username of the owner of the repo, andrepois the name of the repo.
For homework you will use the following packages from CRAN: "tidyverse", "rworldmap", "rworldxtra", "ggmap", "devtools", "rmarkdown", "knitr", "xml2", "rvest", "magrittr", "shiny", "roxygen2", and "miniUI".
Note: Before installing the "devtools" package, you will most certainly need to install building tools.
For Windows, you need to install RTools.
For Mac, you need to install XCode.
Check this link for more details.
Instead of installing these packages one by one, you can pass the vector of characters packages’ names:
pkgs = c("tidyverse", "rworldmap", "rworldxtra", "ggmap", "devtools", "rmarkdown", "knitr", "xml2", "rvest", "magrittr", "shiny", "roxygen2","miniUI")
install.packages(pkgs = pkgs)
Additionally, one has to install packages from "ptdspkg" repo of SMAC-Group GitHub user, and Hadley Wickham’s "emo" package (i.e., by using devtools::install_github("SMAC-Group/ptdspkg") and devtools::install_github("hadley/emo"), respectively).
Note: Packages should be installed only once. No needs to install them every time when you want to use them (it is the same as installing Skype every time you want to call your parents). That is why it is better to do it in concole, not in source editor.
Check yourself: To check if a package was installed successfully, use "name_of_package" %in% rownames(installed.packages()).
2. Installing and setting up Git, GitHub, and GitHub Desktop
In this section we will install a distributed version-control system Git, register a new user at GitHub and connect them together.
2.1 Installing and setting up Git
- Download Git installer for Mac or for Windows.
- Open the downloaded file and follow the proposed steps
Configure your Git to let it know who you are:
git config --global user.name "YOUR FULL NAME" git config --global user.email "YOUR EMAIL ADDRESS"Please do use your UNIL email address, so that we can exploit GitHub Student Developer Pack afterwards.
Check yourself: Type in Terminal: git --version. It should display Git version, (e.g., git version 2.22.0)
Note: For Mac users, Git could be already preinstalled. However, Apple does not provide the latest version, that is why we have just installed the latest Git. If the previous command shows git version 2.7.0 (Apple Git-66), we will need to change the path of the executable command git. To do so execute the following commands in Terminal:
cd ~
touch .bash_profile
echo 'export PATH="/usr/local/bin:${PATH}"' >> .bash_profile
source .bash_profile
Note: Sometimes RStudio has a wrong path to git command. To check it, go to Tools -> Global Options… -> Git/SVN, check the box “Enable version control interface for RStudio projects”. Then, “Git executable” and which git/where git (for Mac/Windows users, respectively) should be the same. Otherwise, copy the path from Terminal to RStudio.
To check if it worked, type which git in Terminal and expect to see /usr/local/bin/git.
2.2 Registering a GitHub account
- Visit https://github.com and fill in the fields. Please use the same email (i.e., UNIL email) address and short username without special symbols like hyphen, periods, etc. Furthermore, use free plan.
Set up an SSH connection follow steps at https://help.github.com/en/articles/generating-a-new-ssh-key-and-adding-it-to-the-ssh-agent and https://help.github.com/en/articles/adding-a-new-ssh-key-to-your-github-account
Set up a GitHub Student Developer Pack by visiting https://education.github.com/discount_requests/new
2.3 Installing and setting up GitHub Desktop
- Visit https://desktop.github.com and download GitHub Desktop
- Install it
- Fill in your username and password
Bonus: connecting Slack to your repo
https://get.slack.help/hc/en-us/articles/232289568-Use-GitHub-with-Slack